Brick masonry is the arrangement of bricks in a specific pattern using mortar to fill the joints. This is commonly used to construct walls, foundations, arches, and other architectural elements.
The type of courses is one of the most important factors that contribute to the overall performance of masonry construction. But why are courses so important?
Choosing the right type of course not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of your home or commercial space but also ensures its structural stability.
Keep exploring this blog to learn more about brick masonry courses and their role in making your construction project durable and visually appealing.
What is a Course in Brick Masonry?
Arranging a layer of uniform units horizontally within a wall is considered a course in brick masonry. Generally, it can be a continuous row of various masonry units, such as concrete masonry units (CMU), stones, bricks, tiles, shingles, and more.
A course in brick masonry involves precisely arranging bricks in a designated horizontal row, which ensures that the brickwork is strong and stable enough to withstand various stresses over time.
Types of Courses in Brick Masonry
Stretcher Courses
This resembles a row of stretchers and is the simplest and most familiar arrangement of masonry units. The stretcher course pattern sits halfway over the joints in the row below.
This is one of the most time- and cost-effective ways to lay bricks. Many can easily notice this pattern more commonly in brick buildings.
Header Courses
This type entirely consists of headers, not the stretcher side of bricks in the course. In simpler terms, masonry units are laid with their ends towards the face of the wall.
Header courses are usually for very high-quality buildings and radial brickwork.
Bond Courses
This type of course is where the brick headers are seen in the facing and backing masonry. This arrangement is important to ensure the structural integrity and stability of the brick walls.
Some types are available in bond courses, such as Flemish Bond, English Bond, Garden Wall Bond, and Stack Bond.
Flemish Bond:
This is created in a single course by laying alternate headers and stretchers. Flemish bond is a traditional course that is also known as Dutch bond.This course attracts many people with the alternative headers and stretcher pattern used for two thick brick walls.
English Bond:
Similar to Flemish bond, English bonds are also the oldest form of brick bonding. They are alternative course arrangements of stretchers and headers. People can witness a row full of headers and another row with stretchers. English bond is considered the strongest course and is widely used for building bridges and other structural projects.
Stack Bond:
This type is widely used for decorative purposes as it has less structural integrity. In a stack pattern, bricks are directly laid on one stretcher over the other.
You can witness stack bonds in garden walls, interior partitions, and visually appealing facades.
Plinth Courses
Plinth courses are ideal for both commercial and residential buildings. A plinth is a portion of the structure between the floor’s surface above the ground and the surrounding ground.
In simple words, the plinth is known as the bottom course of the wall. Plinth levels are essential for a stable foundation for the overall construction of floors and walls.
Materials and Tools Used in Laying a Course
Without tools and materials, brick masons can’t successfully lay a course. Whether you are a property owner or construction professional, understanding the materials and tools ensures safety, design flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and quality of work.
Here are the materials used in laying a course:
Brick
Brick is definitely the most important building material in masonry. Bricks should be tested for durability, hardness, and quality before using them in construction. Evaluating this helps to ensure the building is safe even before beginning the construction.

Mortar
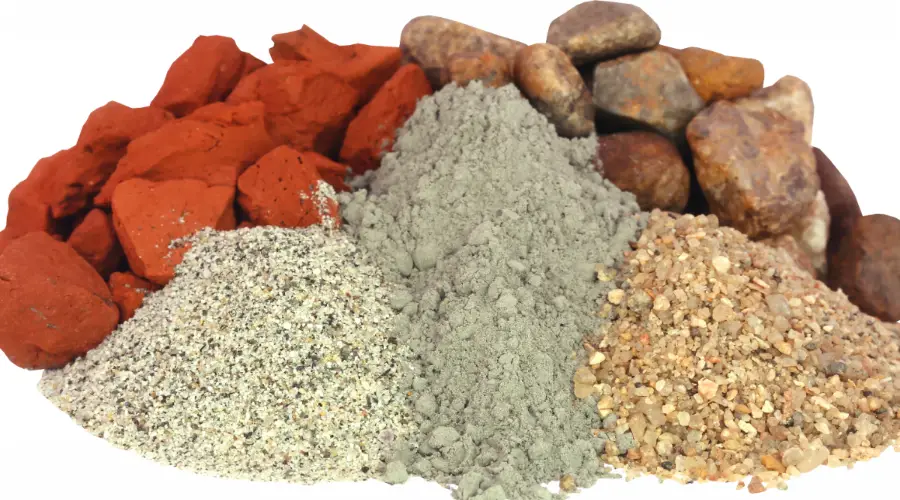

Mortar is nothing but a mixture of sand, cement or lime (a binder), and water to fill the gaps between bricks or stones. This mixture is applied as a paste in between blocks or bricks to bind them together. You might be more familiar with mortar, particularly if you’ve been to construction sites previously.
Now, it’s time to know about the tools used in brick masonry.
Trowel
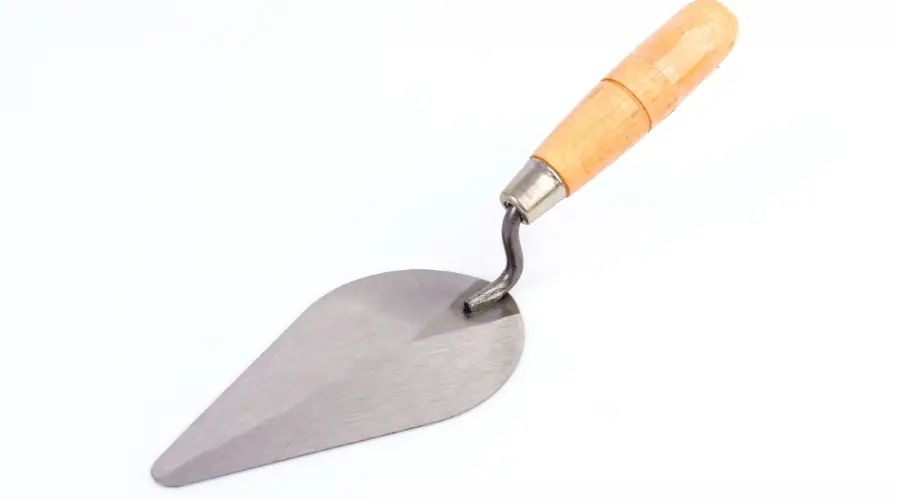

The trowel is a widely used handheld tool in brick masonry. The primary purpose of the trowel is to spread and shape mortar evenly to secure the bonds between bricks.
Brick Hammer
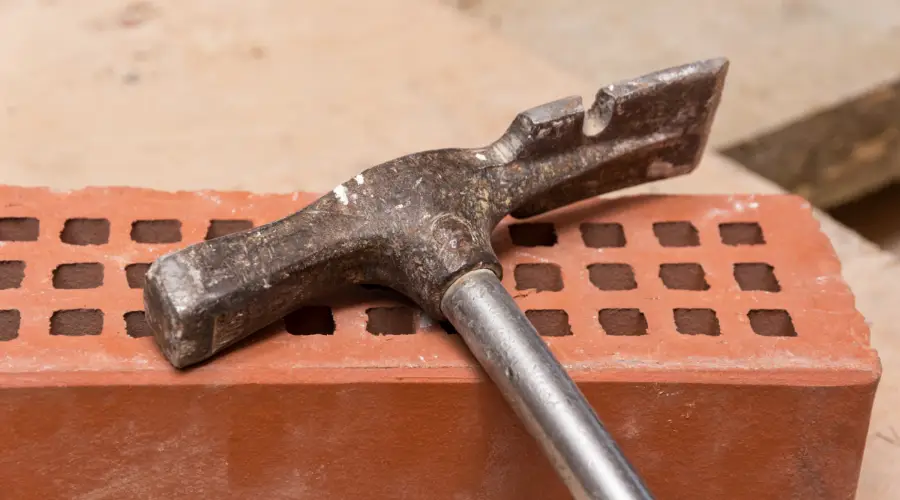

The brick hammer is considered a Mason’s best friend as it has two different faces: a chisel-shaped blade to cut bricks and a flat face to strike and set the bricks evenly.
Steel Tape

This is also the most familiar tool; measuring steel tape ensures the bricks are arranged to the exact length. Even people from the non-construction industry can use it for other purposes.
Mason’s Square
Mason’s square is to ensure the levels and accuracy of two perpendicular surfaces. The tool has a standard reference of 90 degrees to verify the accuracy of the corners.
How to Lay a Course in Brick Masonry
- Work out and finalise how many bricks you need to construct a wall.
- Mix the mortar, add soil, cement, and water, and fix it until you get a smooth and creamy texture. It can be wet but not loose.
- Apply the first layer of mortar along the string line for 1 to 2 cm, which is known as the bedding.
- Start arranging the bricks according to the type of course you need.
- Lay out the bricks in the particular course; it can be a stretcher, header, or English bond.
- Then, apply mortar to arrange the bricks in a specific course. For some courses, you will only need a half-brick, so cut and place the bricks accordingly.
- Repeat the process until you build the wall. Remove the excess mortar on the top and sides of the bricks.
Significance of Courses in Structural Integrity
Structural integrity refers to the strength of a building or structure in holding its components together. Maintaining integrity requires collaborative efforts and consistent evaluation when choosing every material for a construction project.
You need to be conscious of materials and test them for hardness, durability, load and stress analysis, and brick course. Yes, the course is also one of the most important factors in ensuring structural integrity.
It’s because some specific course arrangements can be highly durable and stronger than others. For instance, you can consider English bond brickwork; the alternate courses of headers and stretchers improve its structural integrity, making it suitable for load-bearing walls.
Meanwhile, the stack bond pattern is considered the weakest as the bricks are laid directly on top of one another with the joints aligned. This type of bond is apt for decorative walls and interiors.
Maintenance and Inspection of Brick Courses
Surely, everyone needs to know about the maintenance of brick courses. Property owners need to evaluate their buildings at least once a year, as environmental pollution and exposure to harsh weather conditions are getting worse.
Regular monitoring of brick courses helps to identify even smaller defects, such as small cracks or chips. This identification allows you to take timely action and repair the defects with suitable mortar or filler.
Once you have completely evaluated the building, you can clean it with a soft brush or cloth and repair it with filler.
On the other hand, you can also visit professional services for enhanced cleaning and maintenance. Their services offer many benefits and make cleaning a hassle-free process.
Conclusion
Courses in brick masonry provide several advantages, making them ideal for many construction projects. However, the quality of the bricks, mortar, and other materials used also plays an important role in strengthening the structural integrity.
In that instance, selecting high-quality materials for different types of courses ensures enhanced structural integrity and long-term stability. So, always prioritise the best materials and contractors to get the best results.

